Gas Fireplace Exhaust
Gas fireplaces are popular for their efficiency, convenience, and aesthetic appeal. Unlike traditional wood-burning fireplaces, gas models provide warmth without the hassle of wood logs and extensive cleaning. However, one key aspect of maintaining a gas fireplace is ensuring proper exhaust, which is crucial for both safety and performance. Let’s talk about the details of gas fireplace exhaust systems, explaining their types, functionality, maintenance requirements, and more. Here’s everything you need to know about keeping your gas fireplace exhaust working safely and efficiently.
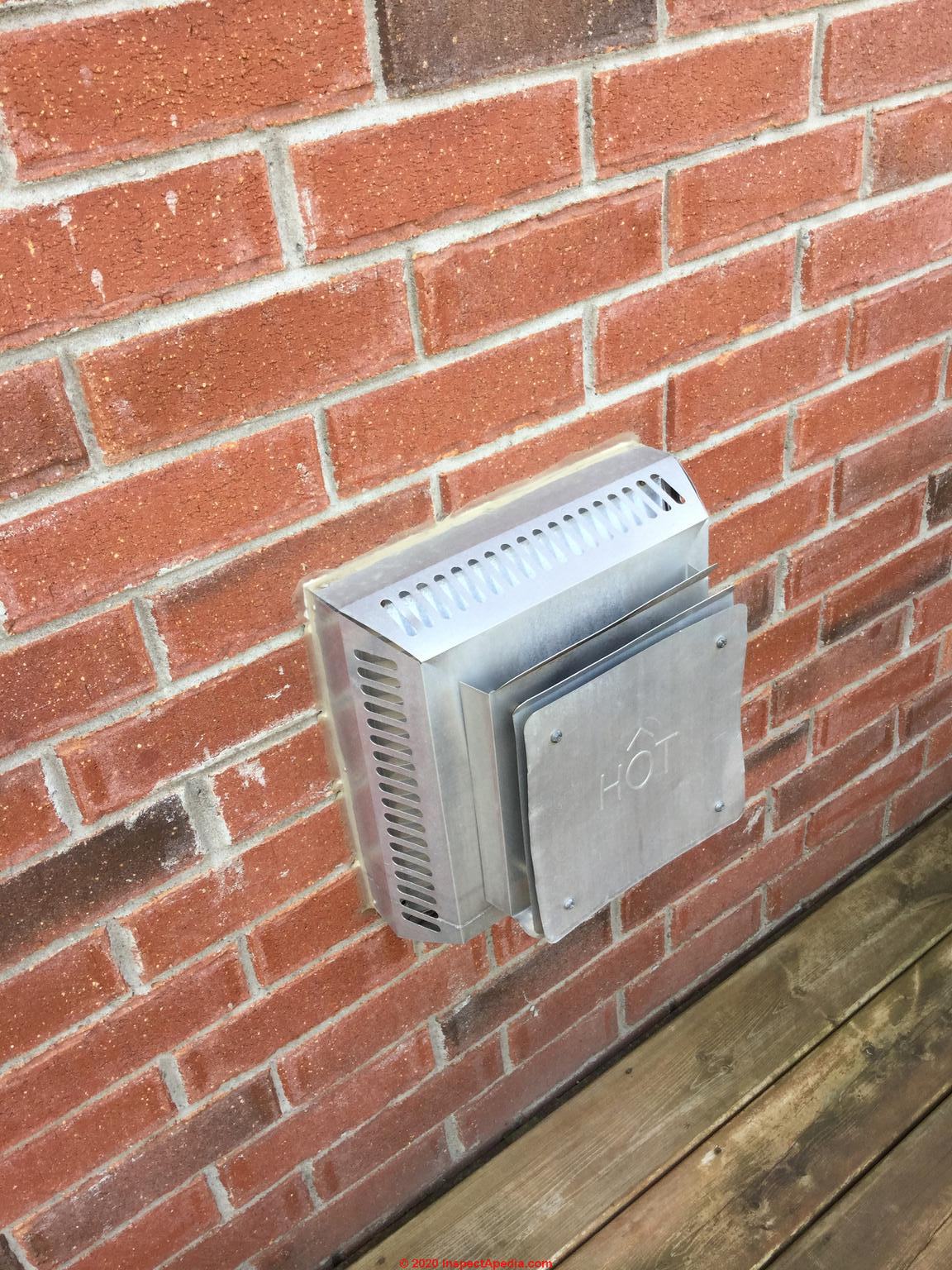

The Importance of Proper Gas Fireplace Exhaust
Gas fireplaces produce combustion byproducts, including carbon monoxide, nitrogen dioxide, and water vapor, all of which must be vented out of the home. The primary function of a gas fireplace exhaust is to remove these harmful gases to maintain indoor air quality and prevent any potential health hazards. Improper or insufficient venting can lead to the buildup of these gases indoors, which poses a serious risk to residents.
In addition to ensuring safety, proper exhaust systems also enhance fireplace efficiency. By expelling combustion byproducts efficiently, the fireplace can draw in fresh air for combustion, allowing it to burn fuel more cleanly and effectively. This helps to keep heating costs down and ensures that the fireplace operates smoothly. Without a reliable exhaust system, the gas fireplace may not function optimally, which can lead to more frequent repairs and higher fuel consumption.
Moreover, a well-maintained exhaust system minimizes the risk of backdrafts, which occur when outside air is pulled back into the home through the vent. This can bring harmful gases indoors, compromising air quality. A properly functioning exhaust system allows the gas fireplace to serve as a safe, dependable, and enjoyable source of warmth for your home.

Types of Gas Fireplace Exhaust Systems
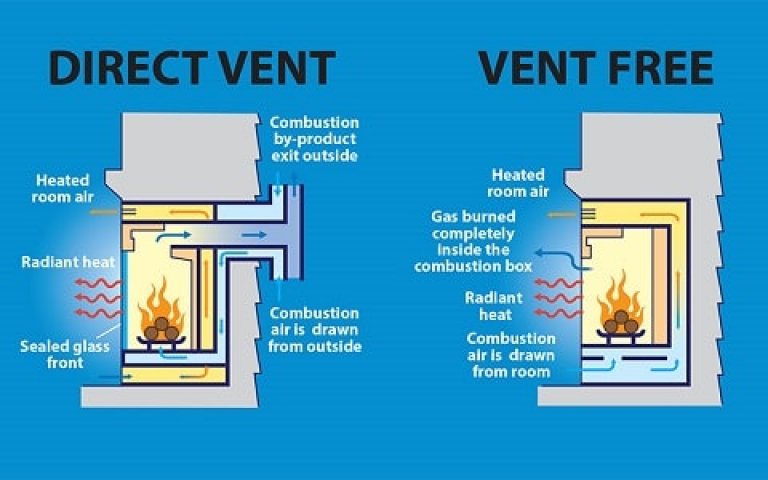
There are three main types of gas fireplace exhaust systems: direct vent, vent-free, and natural vent (also known as B-vent). Each type has unique characteristics, advantages, and potential drawbacks, making it important to select the right one for your home’s needs.
Direct vent systems are the most popular and are known for their efficiency and safety. They use a two-layered pipe system to pull in fresh air from outside for combustion while expelling exhaust gases through an outer pipe. This type of exhaust system is sealed off from the indoor environment, reducing the risk of indoor air contamination and making it ideal for homes with limited ventilation options.
Vent-free or ventless systems, on the other hand, do not have an external exhaust. Instead, they release combustion gases directly into the indoor air. Although these systems are designed to burn gas cleanly, they may still release trace amounts of pollutants. As such, they are subject to strict regulatory standards and are not permitted in certain areas. Vent-free fireplaces are most effective in well-ventilated spaces and are typically more suitable as supplemental heating sources.
Last, natural vent or B-vent systems rely on a flue that goes directly up through the roof, similar to traditional wood fireplaces. These systems use indoor air for combustion and rely on natural draft principles to expel exhaust gases upward. While affordable and relatively easy to install, B-vent systems are not as efficient as direct vent models and may not be ideal for tightly sealed, modern homes.
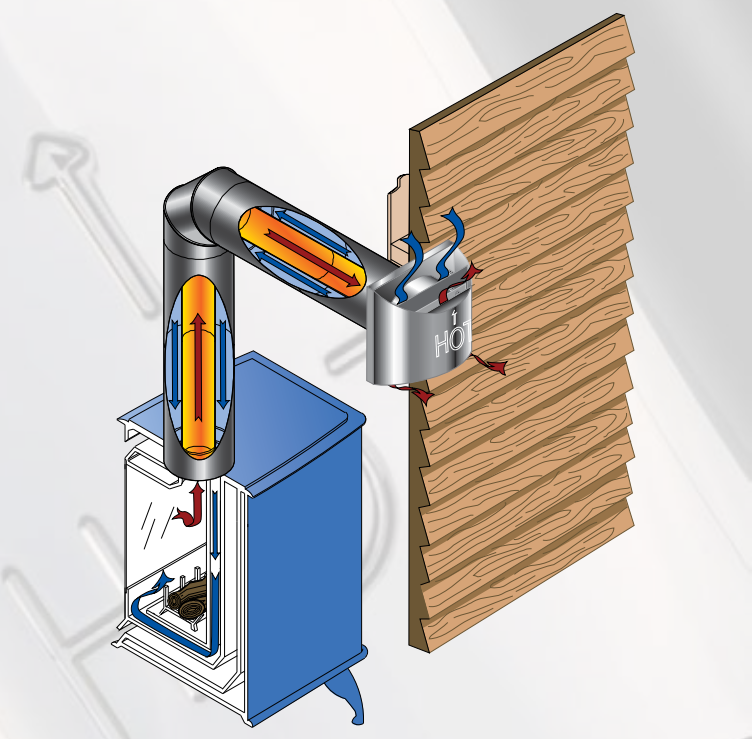
How Gas Fireplace Exhaust Systems Work
Understanding the mechanics of a gas fireplace exhaust system can help homeowners appreciate the importance of maintenance and proper installation. For direct vent fireplaces, the dual-pipe system enables efficient combustion. The inner pipe channels combustion byproducts outward, while the outer pipe draws in fresh air. This arrangement ensures that indoor air quality remains unaffected, making the system safer and more energy-efficient.
In vent-free systems, the combustion process is engineered to produce minimal emissions. These fireplaces often have oxygen depletion sensors (ODS) that shut off the gas if oxygen levels drop too low, ensuring safety. However, vent-free models must be operated with caution, especially in smaller or poorly ventilated spaces. They are also designed with a specific fuel-to-air ratio to minimize emissions, which underscores the importance of proper fuel and usage guidelines.
B-vent or natural vent systems work differently, relying on natural convection to expel exhaust gases. Since these systems use indoor air for combustion, a chimney or vertical flue directs the gases outside. The rising warm air creates a draft that pulls exhaust gases upward and out. While these systems are generally simpler, they may experience backdraft issues if the house is overly sealed or if there is insufficient make-up air, making them less ideal for highly insulated homes.
Installation Considerations for Gas Fireplace Exhausts
Installing a gas fireplace exhaust system is a task best left to professionals, as improper installation can lead to issues like gas leaks, back-drafting, and inadequate venting. One of the first considerations during installation is choosing the right location. For direct vent fireplaces, an external wall is ideal because it minimizes the need for extensive venting infrastructure, reducing both installation time and costs. However, if installation on an external wall is not feasible, routing vent pipes through the roof can also be an option.
Clearance and proximity to flammable materials are also critical. Local building codes and manufacturer instructions will provide guidelines on safe clearances, including the distance between venting components and combustible materials like wood framing. Adequate spacing helps prevent the buildup of excessive heat and reduces the risk of fire. For natural vent fireplaces, chimney clearance, and height are especially important to create a proper draft and avoid downdrafts.
Additionally, installing a carbon monoxide detector is highly recommended, regardless of the venting system used. Even with well-installed exhaust systems, a carbon monoxide detector adds an extra layer of safety by alerting occupants to any potential issues. Following manufacturer guidelines and local codes, along with regular inspections, can help keep the fireplace exhaust system working efficiently and safely.

Maintenance and Inspection of Gas Fireplace Exhausts
Routine maintenance and inspections are essential to ensure the longevity and efficiency of a gas fireplace exhaust system. Annual inspections by a certified technician can help detect and address issues such as blockages, corrosion, and vent pipe deterioration. During these inspections, technicians will check for leaks, inspect the seals, and clean the venting components to keep everything in good working order.
Cleaning the exhaust system is particularly important for direct vent and B-vent fireplaces. Over time, soot and debris can accumulate in the pipes, obstructing airflow and reducing efficiency. In some cases, bird nests or leaves can block the flue, creating a potential hazard. Keeping the venting system clear ensures that the fireplace operates smoothly, providing consistent warmth without the risk of combustion byproducts entering the home.
For vent-free fireplaces, the primary maintenance task is checking the oxygen depletion sensor and ensuring that the air intake areas are not obstructed. Since vent-free models rely on indoor air, keeping the area well-ventilated and free from dust or debris is essential. Homeowners should also periodically inspect any visible connections for signs of wear or damage. This hands-on maintenance approach helps extend the life of the system and maintains optimal indoor air quality.
Common Issues and Troubleshooting for Gas Fireplace Exhausts
Like any home appliance, gas fireplace exhaust systems can sometimes encounter problems. One common issue is back drafting, which occurs when outdoor air flows back into the home through the vent, potentially carrying harmful gases with it. This issue is often linked to poor airflow or a blocked vent. In cases of back drafting, homeowners should check for obstructions in the vent pipe and ensure that the home has adequate ventilation.
Another issue is pilot light failure, which can sometimes be traced to poor exhaust performance. If the venting system is not removing combustion byproducts effectively, it can interfere with the pilot light, causing it to go out. This can be resolved by cleaning or adjusting the vent components to ensure proper airflow. However, it’s best to consult a professional if issues persist, as a malfunctioning pilot light could indicate broader exhaust or gas supply problems.
Finally, excessive condensation on windows or walls around the fireplace may indicate an exhaust problem, especially in vent-free systems. High humidity levels and inadequate ventilation can lead to moisture buildup, which is a sign that the exhaust system is not effectively managing combustion byproducts. Addressing this issue may involve improving ventilation or adjusting the use of the fireplace to prevent excess moisture accumulation indoors. Regular maintenance and prompt troubleshooting can help resolve these common exhaust issues, ensuring that the gas fireplace remains a safe and effective heating solution.

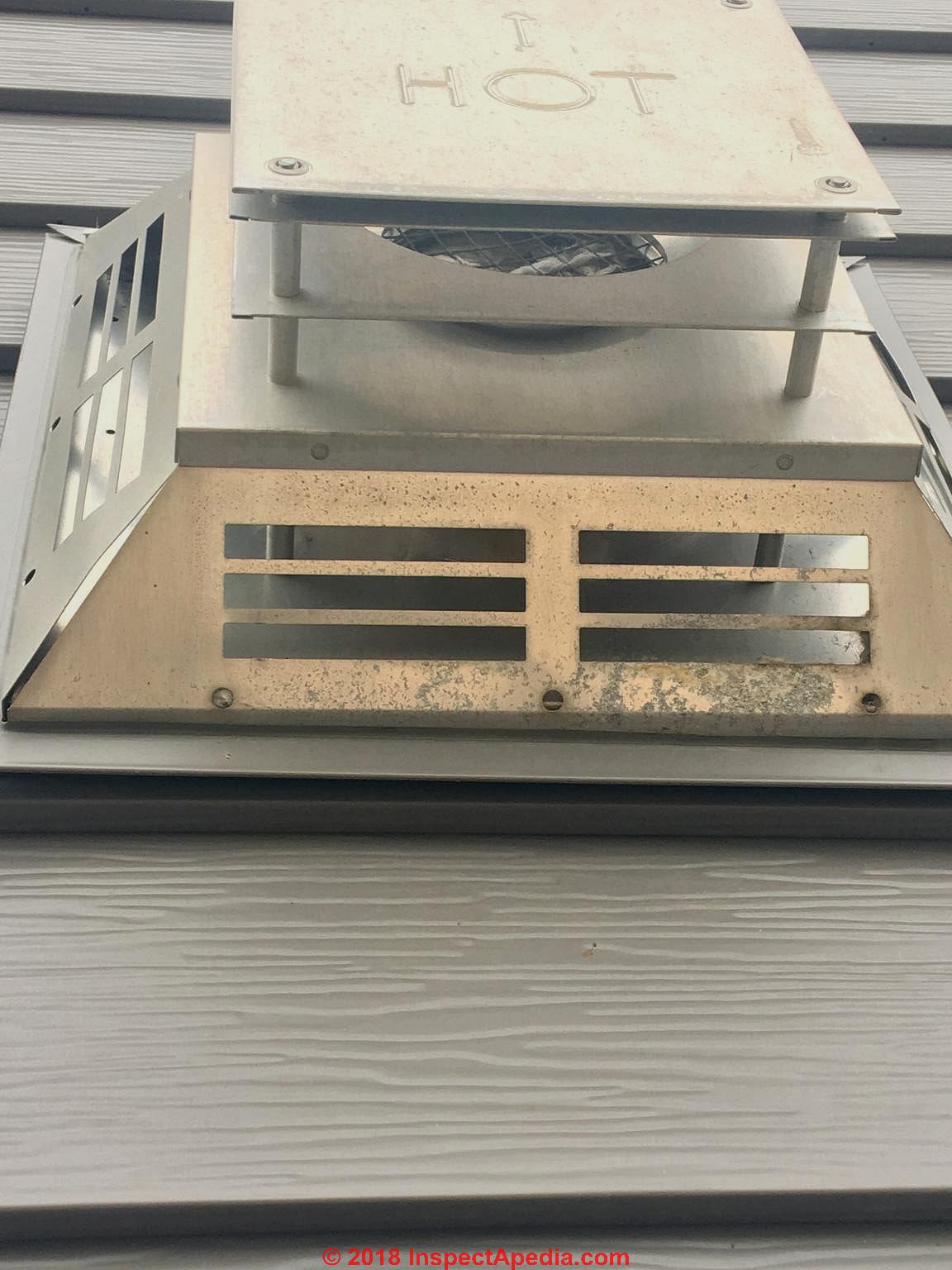
Gas fireplace wall exhaust clearance
Gas Fireplace Vent Cap Clearance Distance FAQs

Duluth Forge Vent-Free Stainless Outdoor Gas Fireplace Insert With Black Fire Glass Media

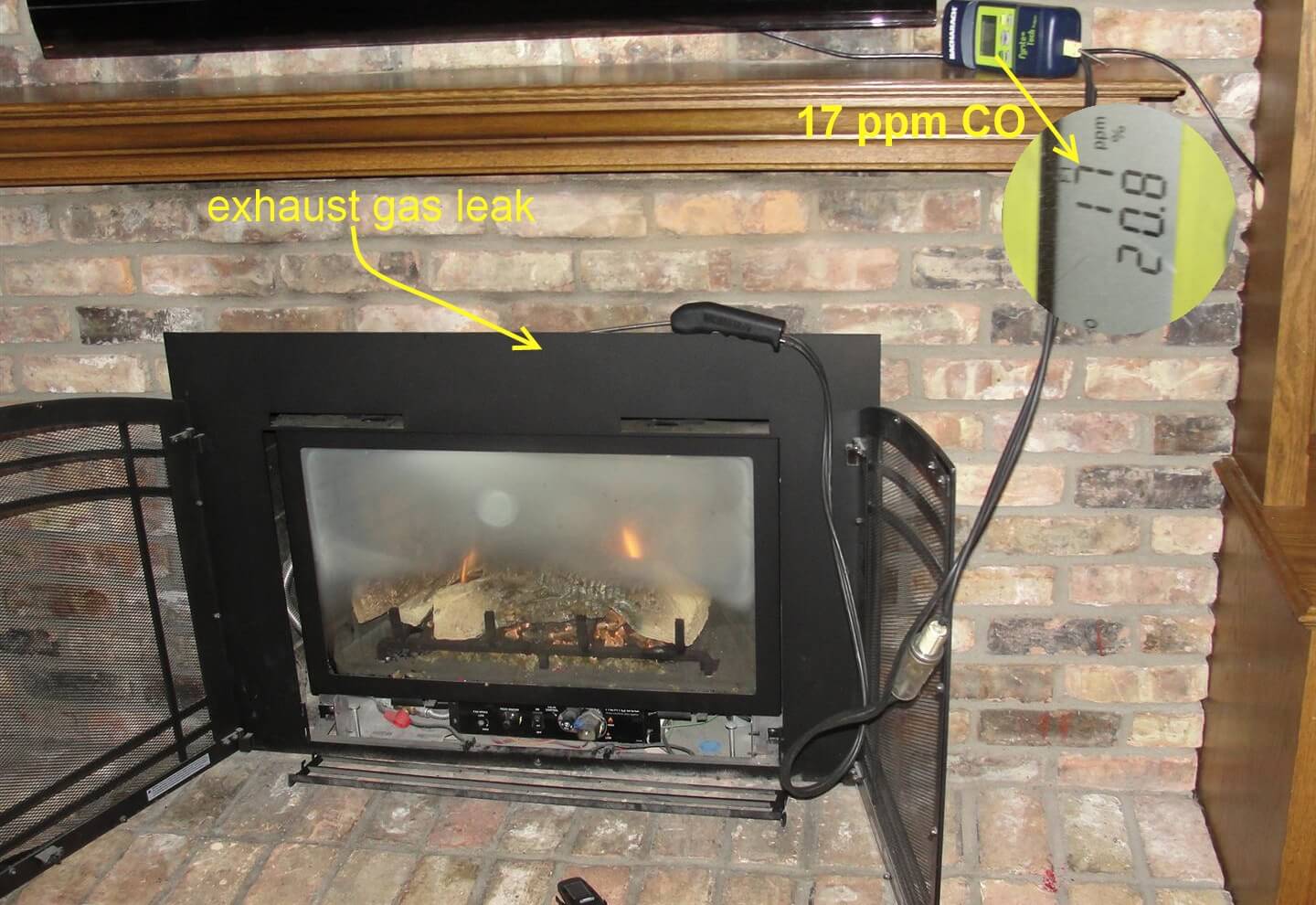
“If there’s a CO problem in my home, why didn’t the CO alarms go off?”

Gas Fireplace (Ultimate Design Guide) – Designing Idea

Wasps in my gas fireplace exhaust (fireplaces, light, steel, building) – House -remodeling

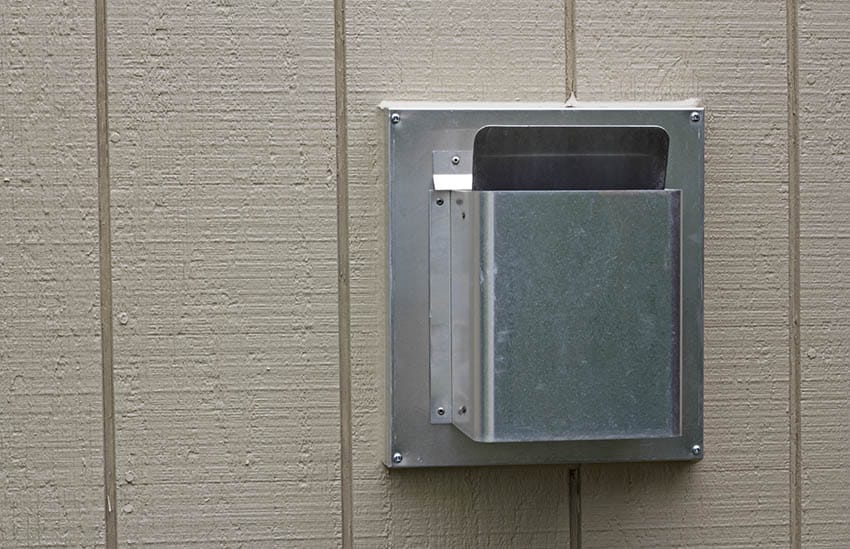
Fireplace Exhaust Pipes

Related Posts:
- Fireplace Gas Valve Extension
- Antique Gas Fireplace Heater
- Gas Fireplace Leak Repair
- Gas Fireplace Venting Code
- Gas Fireplace Inserts with Blower Fan
- Gas Fireplace Heat Exchanger
- Gas Fireplace Trim
- Gas Fireplace Not Starting
- Gas Fireplace B&Q
- Valor Gas Fireplace Remote Control
A gas fireplace exhaust is an essential component of a gas fireplace system that helps to safely and efficiently vent out combustion byproducts, such as carbon monoxide and other harmful gases, from the home. It is crucial to have a properly installed and maintained gas fireplace exhaust to ensure the safety of your household. In this guide, we will discuss the benefits, pros and cons, common mistakes to avoid, and frequently asked questions related to gas fireplace exhaust systems.
Benefits of Gas Fireplace Exhaust:
Safety: One of the primary benefits of a gas fireplace exhaust is that it helps to remove harmful gases produced during the combustion process, such as carbon monoxide. Proper ventilation is essential to prevent these gases from accumulating in your home and posing a serious health risk to you and your family.
Efficiency: A well-designed and properly installed gas fireplace exhaust can help improve the overall efficiency of your gas fireplace system. By venting out combustion byproducts effectively, the exhaust system ensures that your fireplace operates at its optimal performance level, providing you with consistent heat output while reducing energy waste.
Comfort: With a functioning gas fireplace exhaust, you can enjoy the warmth and ambiance of your fireplace without worrying about indoor air quality issues. The exhaust system helps maintain a comfortable indoor environment by removing moisture, odors, and other pollutants generated during the burning process.
Compliance: Many local building codes and regulations require homeowners to have a properly functioning gas fireplace exhaust in place to comply with safety standards. By ensuring that your gas fireplace exhaust is in good working condition, you can avoid potential fines or violations from regulatory authorities.
Pros and Cons of Gas Fireplace Exhaust:
Pros:
– Provides safe ventilation for combustion byproducts
– Improves energy efficiency of the gas fireplace system
– Enhances indoor air quality and comfort
– Ensures compliance with building codes and regulations
Cons:
– Requires regular maintenance and cleaning to prevent blockages
– May incur additional installation costs for complex venting systems
– Can be affected by external factors such as weather conditions
– Improper installation or maintenance can lead to safety hazards
Common Mistakes to Avoid with Gas Fireplace Exhaust:
Neglecting regular maintenance: Failure to schedule annual inspections and cleanings for your gas fireplace exhaust can result in blockages or malfunctions that compromise its effectiveness.
Using incorrect venting materials: It is essential to use the proper venting materials recommended by the manufacturer for your specific gas fireplace model to ensure safe and efficient operation.
Ignoring warning signs: Pay attention to any unusual odors, sounds, or visual cues coming from your gas fireplace exhaust system, as these could indicate potential issues that require immediate attention.
Attempting DIY repairs: Gas fireplace exhaust systems should only be serviced by qualified professionals who have the necessary training and expertise to handle complex ventilation components safely.
How often should I clean my gas fireplace exhaust?
It is recommended to have your gas fireplace exhaust inspected and cleaned at least once a year by a certified technician to ensure optimal performance and safety.
Can I install my own gas fireplace exhaust system?
Installation of a gas fireplace exhaust should be performed by a licensed professional who has experience working with venting systems to guarantee proper function and compliance with local codes.
What are some signs that my gas fireplace exhaust needs repair?
Common indicators of potential issues with your gas fireplace exhaust include soot buildup around the vent, unusual odors or noises during operation, or difficulty lighting the pilot light.
Do I need a chimney for a gas fireplace exhaust?
Gas fireplaces typically do not require a traditional chimney but rely on direct venting systems or other specialized flue configurations designed for the efficient removal of combustion byproducts.
Ensuring that your gas fireplace exhaust is properly installed, maintained, and functioning is crucial for the safety, efficiency, and comfort of your home. By understanding the benefits, pros and cons, common mistakes to avoid, and frequently asked questions related to gas fireplace exhaust systems, you can make informed decisions about caring for this vital component of your heating system. Remember to always consult with a professional HVAC technician or fireplace installer if you have any concerns or questions about your gas fireplace exhaust system. Regular maintenance and inspections are key to ensuring that your gas fireplace operates safely and efficiently, providing you with reliable warmth and comfort during the colder months. By following these guidelines and best practices, you can enjoy the many benefits of a well-maintained gas fireplace exhaust for years to come.